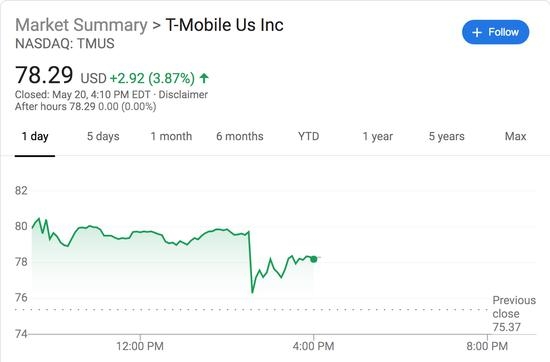
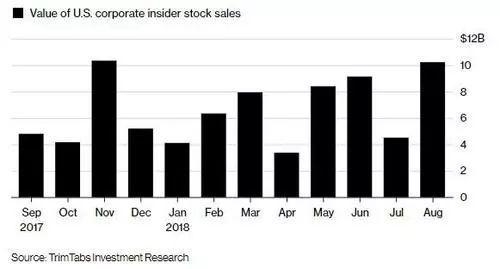
In the United States, stock ownership has become an integral part of the financial landscape, with millions of individuals investing in the stock market. This article delves into the statistics of stock ownership in the US, highlighting the demographics and factors contributing to this trend.
Stock Ownership Trends in the US
According to a report by the Federal Reserve, as of 2021, approximately 55% of American households owned stocks, either directly or indirectly through retirement accounts. This represents a significant increase from the 48% of households that owned stocks in 2010.
Demographics of Stock Owners
The demographics of stock owners in the US vary widely. While older individuals, particularly those aged 65 and above, are more likely to own stocks, the trend is shifting towards younger generations. A study by the Investment Company Institute (ICI) found that 36% of individuals aged 18-29 owned stocks in 2020, up from 28% in 2010.
Retirement Accounts and Stock Ownership
Retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, play a crucial role in the rise of stock ownership in the US. These accounts offer tax advantages and automatic contributions, making it easier for individuals to invest in the stock market. According to the ICI, 401(k) plans held approximately $7.8 trillion in assets as of 2021, with a significant portion invested in stocks.
Factors Contributing to Stock Ownership
Several factors have contributed to the rise in stock ownership in the US:
- Economic Growth: The US economy has experienced steady growth over the past few decades, leading to increased wealth and disposable income for many Americans.
- Financial Education: There has been a growing emphasis on financial literacy, with more individuals seeking to understand the stock market and make informed investment decisions.
- Technology: The advent of online brokers and mobile trading apps has made it easier for individuals to invest in the stock market without the need for a financial advisor.
Case Studies
- The Great Recession: The financial crisis of 2008 had a significant impact on stock ownership in the US. Many individuals lost their retirement savings, leading to a decrease in stock ownership. However, as the economy recovered, stock ownership began to rise again.
- The COVID-19 Pandemic: The pandemic caused a sharp decline in stock prices, but as the economy began to recover, many investors took advantage of the lower prices to increase their stock holdings.
Conclusion
Stock ownership in the US has reached an all-time high, with millions of individuals investing in the stock market. The trend is likely to continue as economic growth, financial education, and technology continue to drive this trend. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding the demographics and factors contributing to stock ownership can help you make informed investment decisions.
Last Day to Sell Stock for Tax Loss in 2018? us stock market today