Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of the financial market, one question that often comes to the forefront is whether the US stock market is overvalued. This article delves into this critical topic, examining various factors that contribute to the valuation of stocks and providing insights into the current state of the US stock market.
Understanding Stock Valuation
Stock valuation is a complex process that involves assessing the intrinsic value of a company's shares. It is influenced by several factors, including the company's financial health, industry trends, economic conditions, and market sentiment. Several valuation models, such as the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio and Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio, are commonly used to gauge whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued.
Historical Perspective
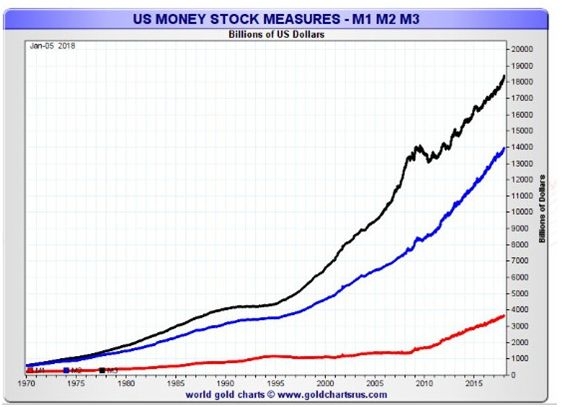
To determine whether the US stock market is overvalued, it is essential to consider historical data. Over the past few decades, the US stock market has experienced several bull and bear markets. During the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s, the market was widely considered to be overvalued, leading to a significant crash in 2000. Similarly, the market experienced another period of overvaluation leading up to the 2008 financial crisis.
Current Market Conditions
As of 2023, the US stock market is facing several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the high level of corporate debt. Many companies have taken on substantial debt to finance their operations and expansion, which could lead to financial distress if economic conditions deteriorate.
Moreover, the P/E ratio of the S&P 500 has been consistently above its long-term average of 16. This suggests that stocks are currently overvalued, as investors are paying a premium for shares relative to the company's earnings.
Economic Factors
Economic factors also play a crucial role in determining the valuation of stocks. Inflation, interest rates, and economic growth are key indicators that can impact the market. For instance, rising inflation can erode purchasing power, leading to a decrease in stock prices. Similarly, higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, affecting corporate profitability and, consequently, stock prices.
Market Sentiment

Market sentiment is another critical factor that can influence stock valuations. During periods of optimism, investors are willing to pay higher prices for stocks, leading to overvaluation. Conversely, during periods of pessimism, stocks can become undervalued.
Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of overvaluation on the stock market, let's consider two case studies:
Tech Stocks in the Late 1990s: The dot-com bubble of the late 1990s saw tech stocks soaring to record highs. Many investors believed that these companies would continue to grow at an exponential rate. However, the market eventually corrected, and many tech stocks lost a significant portion of their value.
Real Estate Stocks Leading Up to the 2008 Financial Crisis: In the years leading up to the 2008 financial crisis, real estate stocks were considered to be overvalued. The excessive lending and speculation in the real estate market eventually led to a housing bubble, which burst, causing a severe economic downturn.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether the US stock market is overvalued is a complex one. While several factors suggest that the market may be overvalued, it is essential to consider historical data, economic conditions, and market sentiment to form a well-informed opinion. Investors should exercise caution and conduct thorough research before making investment decisions.
Daily Life on an US Navy Aircraft Carrier: ? new york stock exchange