In the realm of economics, the concept of stock plays a pivotal role in understanding the dynamics of markets and the behavior of investors. This article delves into the essence of stock in economics, exploring its significance, functions, and impact on the economy. By examining various aspects of stock, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of its role in shaping economic landscapes.
What is Stock in Economics?
In economics, stock refers to the quantity of a particular good or asset at a given point in time. Unlike flow variables, which are measured over a period, stocks are static measures. For instance, the stock of goods in a warehouse or the stock of shares in a company are examples of stock variables.
The Significance of Stock in Economics
Market Dynamics: The stock of goods and assets in an economy influences market dynamics. For instance, an increase in the stock of goods can lead to lower prices, as suppliers compete to sell their products. Conversely, a decrease in stock can drive prices up.
Investment Decisions: The stock of shares in a company is crucial for investors. It determines the market capitalization, which is the total value of a company's outstanding shares. Investors use this information to make informed decisions about buying, selling, or holding stocks.
Economic Growth: The stock of capital goods, such as machinery and equipment, is essential for economic growth. An increase in the stock of capital goods can lead to higher productivity and output, contributing to economic expansion.
Functions of Stock in Economics
Inventory Management: Businesses use stock to manage their inventory levels. By maintaining an optimal stock of goods, companies can minimize costs associated with holding excess inventory and reduce the risk of stockouts.
Production Planning: The stock of raw materials and intermediate goods is crucial for production planning. Companies need to ensure that they have enough stock to meet production demands without incurring excessive costs.
Investment Analysis: Investors analyze the stock of shares in a company to assess its financial health and growth potential. Key metrics like book value per share, price-to-book ratio, and earnings per share are derived from the stock of shares.
Impact of Stock on the Economy
Inflation: The stock of money in an economy can influence inflation. An increase in the stock of money can lead to higher prices, as there is more money chasing the same amount of goods and services.
Unemployment: The stock of labor in an economy affects unemployment rates. An increase in the stock of labor can lead to higher unemployment, as the demand for labor may not keep pace with the supply.
Growth: The stock of capital goods and investment in stocks can drive economic growth. An increase in the stock of capital goods can lead to higher productivity and output, contributing to economic expansion.
Case Studies
Amazon: Amazon's stock has been a major driver of its growth. By maintaining a large stock of goods, the company can fulfill orders quickly and efficiently, leading to increased customer satisfaction and market share.
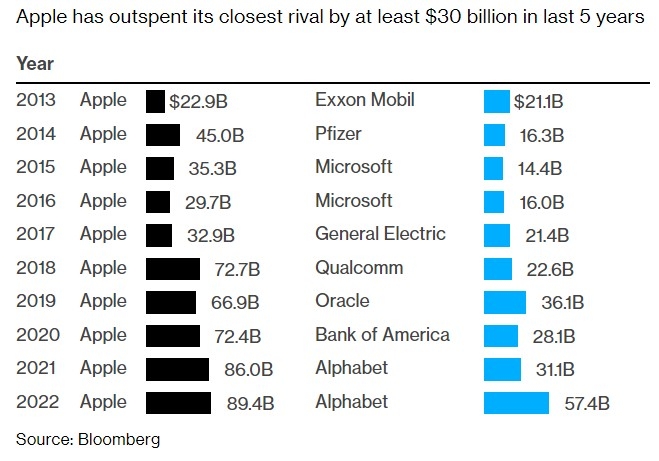
Apple: Apple's stock has been a favorite among investors due to its strong financial performance and growth potential. The company's stock of products, such as iPhones and iPads, has been a key driver of its success.
In conclusion, stock in economics plays a crucial role in shaping market dynamics, investment decisions, and economic growth. By understanding the significance and functions of stock, we can gain valuable insights into the complexities of the economy.
US Global Jets ETF Stock Price: What You Ne? can foreigners buy us stocks